Sunday, June 16, 2024
Thursday, December 24, 2020
OHS the plug-ins do not fail over
CAUSE
The multiple invocations had nothing to do with OSB, rather with the configuration of the plugin for the Apache load balancer. This is expected behavior for the default 11g configuration in certain situations. The issue is due to the use of the plugin configuration parameter "Idempotent".
When "Idempotent" is turned on, the plugin will attempt to resend the HTTP request after it has timed out (configured in the "WLIOTimeoutSecs" parameter in plugin).
http://download.oracle.com/docs/cd/E13222_01/wls/docs100/plugins/plugin_params.html
Unsolicited multiple invocations like this have been reported in other products using the same load balancer configuration.
SOLUTION
- Turn OFF Idempotent in the web server plugin configuration.
http://download.oracle.com/docs/cd/E13222_01/wls/docs100/plugins/plugin_params.html
If "Idempotent" is set to “OFF” the plugin will not fail over. - If not explicitly set, WLIOTimeoutSecs defaults to 300 seconds (5 minutes).
You can add a line in the file httpd.conf ($ORACLE_INSTANCE/config/OHS/ohsx) in order to set this parameter WLIOTimeoutSecs
Wednesday, December 23, 2020
OHS Terminating SSL Requests
Terminating SSL Requests
The following sections describe how to terminate requests using SSL before or within Oracle HTTP Server, where the mod_wl_ohs module forwards requests to WebLogic Server. Whether you terminate SSL before the request reaches Oracle HTTP Server or when the request is in the server, depends on your topology. A common reason to terminate SSL is for performance considerations when an internal network is otherwise protected with no risk of a third-party intercepting data within the communication. Another reason is when WebLogic Server is not configured to accept HTTPS requests.
This section includes the following topics:
About Terminating SSL at the Load Balancer
If you are using another device such as a load balancer or a reverse proxy which terminates requests using SSL before reaching Oracle HTTP Server, then you must configure the server to treat the requests as if they were received through HTTPS. The server must also be configured to send HTTPS responses back to the client.
Figure 9-1 illustrates an example where the request transmitted from the browser through HTTPS to WebLogic Server. The load balancer terminates SSL and transmits the request as HTTP. Oracle HTTP Server must be configured to treat the request as if it was received through HTTPS.
Figure 9-1 Terminating SSL Before Oracle HTTP Server
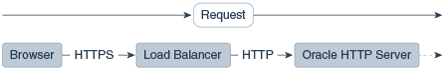
Description of "Figure 9-1 Terminating SSL Before Oracle HTTP Server"
Terminating SSL at the Load Balancer
To instruct the Oracle HTTP Server to treat requests as if they were received through HTTPS, configure the httpd.conf file with the SimulateHttps directive in the mod_certheaders module.
For more information on mod_certheaders module, see mod_certheaders Module—Enables Reverse Proxies.
Note:
This procedure is not necessary if SSL is configured on Oracle HTTP Server (that is, if you are directly accessing Oracle HTTP Server using HTTPS).
- Configure the
httpd.confconfiguration file with the external name of the server and its port number, for example:ServerName <www.company.com:port>
- Configure the
httpd.confconfiguration file to load themod_certheadersmodule, for example:On UNIX:
LoadModule certheaders_module libexec/mod_certheaders.so
On Windows:
LoadModule certheaders_module modules/ApacheModuleCertHeaders.dll AddModule mod_certheaders.c
Note:
Oracle recommends that the
AddModuleline should be included with otherAddModuledirectives.
- Configure the
SimulateHttpsdirective at the bottom of thehttpd.conffile to send HTTPS responses back to the client, for example:# For use with other load balancers and front-end devices: SimulateHttps On
- Restart Oracle HTTP Server and test access to the server. Especially, test whether you can access static pages such as
https://host:port/index.htmlTest your configuration as a basic setup. If you are having issues, then you should troubleshoot from here to avoid overlapping with other potential issues, such as with virtual hosting.
- Ideally, you may want to configure a
VirtualHostin thehttpd.conffile to handle all HTTPS requests. This separates the HTTPS requests from the HTTP requests as a more scalable approach. This may be more desirable in a multi-purpose site or if a load balancer or other device is in front of Oracle HTTP Server which is also handling both HTTP and HTTPS requests.The following sample instructions load the
mod_certheadersmodule, then creates a virtual host to handle only HTTPS requests.# Load correct module here or where other LoadModule lines exist: LoadModule certheaders_module libexec/mod_certheaders.so # This only handles https requests: <VirtualHost <name>:<port> # Use name and port used in url: ServerName <www.company.com:port> SimulateHttps On # The rest of your desired configuration for this VirtualHost goes here </VirtualHost> - Restart Oracle HTTP Server and test access to the server, First test a static page such as
https://host:port/index.htmland then your test your application.
About Terminating SSL at Oracle HTTP Server
If SSL is configured in Oracle HTTP Server but not on Oracle WebLogic Server, then you can terminate SSL for requests sent by Oracle HTTP Server.
The following figures illustrate request flows, showing where HTTPS stops. In Figure 9-2, an HTTPS request is sent from the browser. The load balancer transmits the HTTPS request to Oracle HTTP Server. SSL is terminated in Oracle HTTP Server and the HTTP request is sent to WebLogic Server.
Figure 9-2 Terminating SSL at Oracle HTTP Server—With Load Balancer
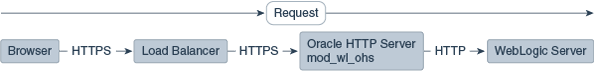
Description of "Figure 9-2 Terminating SSL at Oracle HTTP Server—With Load Balancer"
In Figure 9-3 there is no load balancer and the HTTPS request is sent directly to Oracle HTTP Server. Again, SSL is terminated in Oracle HTTP Server and the HTTP request is sent to WebLogic Server.
Figure 9-3 Terminating SSL at Oracle HTTP Server—Without Load Balancer
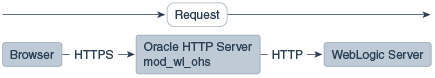
Description of "Figure 9-3 Terminating SSL at Oracle HTTP Server—Without Load Balancer"
Terminating SSL at Oracle HTTP Server
To instruct the Oracle HTTP Server to treat requests as if they were received through HTTPS, configure the WLSProxySSL directive in the mod_wl_ohs.conf file and ensure that the SecureProxy directive is not configured.
- Configure the
mod_wl_ohs.conffile to add theWLSProxySSLdirective for the location of your non-SSL configured managed servers.For example:WLProxySSL ON
- If using a load balancer or other device in front of Oracle HTTP Server (which is also using SSL), you might need to configure the
WLProxySSLPassThroughdirective instead, depending on if it already setsWL-Proxy-SSL.For example:WLProxySSLPassThrough ON
For more information, see your load balancer documentation. For more information on WLProxySSLPassThrough, see Parameters for Oracle WebLogic Server Proxy Plug-Ins in Using Oracle WebLogic Server Proxy Plug-Ins.
- Ensure that the
SecureProxydirective is not configured, as it will interfere with the intended communication between the components.This directive is to be used only when SSL is used throughout. TheSecureProxydirective is commented out in the following example:# To configure SSL throughout (all the way to WLS): # SecureProxy ON # WLSSLWallet "<Path to Wallet>"
- Enable the WebLogic Plug-In flag for your managed servers or cluster.By default, this option is not enabled. Complete the following steps to enable the WebLogic Plug-In flag:
- Log in to the Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console.
- In the Domain Structure pane, expand the Environment node.
- Click on Clusters.
- Select the cluster to which you want to proxy requests from Oracle HTTP Server.The Configuration: General tab appears.
- Scroll down to the Advanced section, expand it.
- Click Lock and Edit.
- Set the WebLogic Plug-In Enabled to yes.
- Click Save and Activate the Changes.
- Restart the servers for the changes to be effective.
- Restart Oracle HTTP Server and test access to a Java application.For example:
https://host:port/path/application_name.
Tuesday, July 21, 2020
Import DUMP file in Oracle
- Create user and grant permission
alter session set "_ORACLE_SCRIPT"=true;
create user [username] identified by [password];
grant connect, create session, imp_full_database to [username];
CREATE SMALLFILE TABLESPACE [TABLESPACE_NAME] DATAFILE 'FILEDATA.dbf' SIZE 7G AUTOEXTEND ON NEXT 100M MAXSIZE UNLIMITED LOGGING EXTENT MANAGEMENT LOCAL SEGMENT SPACE MANAGEMENT AUTO;
GRANT UNLIMITED TABLESPACE TO [username]; - Create Directory
CREATE DIRECTORY BACKUP_DIR AS '/home/oracle/import';
GRANT read,write on DIRECTORY BACKUP_DIR to [username]; - Import
impdp [username]/[password] DIRECTORY=BACKUP_DIR DUMPFILE=File.dmp FULL=Y LOGFILE=import.log
Sunday, February 23, 2020
Oracle OSB 12C - OSB Always Adds a "Charset=Iso-8859-1" to the Content-Type Header
For 12c you'll need to apply below patches:
- Patch 25434715: Forward Porting Bug 18729796 to 12.2.1.x.x release, which addresses the HTTP inbound case.
- Patch 26628960: Cont of Bug 26591735 (Remove charset=utf-8 in Content-Type for Outbound...), which addresses the HTTP Outbound case.
- And add Startup parameter: -Dcom.bea.wli.sb.kernel.charsetRequired=false( in setDomainEnv.sh)
- Remove encoding in business if you have
IBM Integration Bus- Database Definition
Securing database connections
Download JDBC driver for type 4 connections
Setting up a JDBC provider for type 4 connections
Create Database Definition
Install and use xorg-server on macOS via Homebrew
The instructions to install and use xorg-server on macOS via Homebrew: Install Homebrew (if you haven't already): /bin/bash -c ...

-
Ref: https://blogs.sap.com/2016/11/25/get-to-know-camels-simple-expression-language-in-hci/ Introduction Simple is a, well, simple express...
-
WebRequest The function sends an HTTP request to a specified server. The function has two versions: 1. Sending simple requests of typ...
-
Ref:https://www.gtk.org/docs/installations/windows/#using-gtk-from-msys2-packages Installation The MSYS2 project provides a UNIX-like de...




